When the application development process is completed, it’s high time to introduce your special product to the world. First publishing may be thrilling and tricky. Don’t worry. Today we will guide you through the release process on the Google Play Store, which is undoubtedly the leader in the number of published apps and users.
First, we’d like to give you precious advice: do not postpone some crucial tasks until the release or pre-release date. Completing them in advance will save you time and nerves.
And now, let’s get started with publishing your very first Android app.
So, let’s get started!
Step 1: Create a Google Developer account
This is something you can do at the beginning of the app development process. Without registering a Google Developer Account, you can’t publish your app on Google Play.
You can use any of your current Google accounts or create another one to sign up for a Google Developer Account. It doesn’t matter whether it’s a private or corporate account. You may easily transfer your app to another one in the future.
The creation process includes signing the Google Play Developer distribution agreement, adding some personal information, and paying a one-time registration fee of $25. There is nothing complicated. Just follow the instructions.
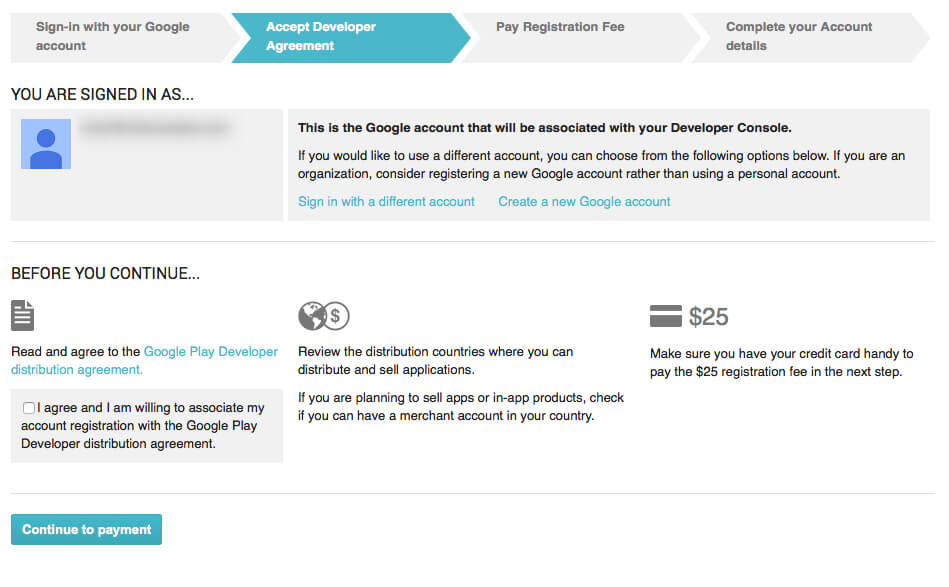
Google Play Developer distribution agreement
Usually, it takes no more than two days to get approval from Google. Don’t worry if you forget to add some information. You can edit your account later.
Step 2: Add a Merchant Account
If you plan to sell paid apps or in-app purchases, you have to create a Google Merchant Account. There you can manage app sales and your monthly payouts, as well as analyze sales reports.
Once you finish creating the Merchant profile, the developer account gets automatically linked to it.
Step 3: Prepare the Documents
Paperwork always requires much effort, especially when it comes to any kind of legal documents. Based on our experience, we highly recommend starting to prepare the End User License Agreement (EULA) and Privacy Policy in advance.
You can take the documents from similar apps as references and create your own based on them, or ask a lawyer to make everything from scratch.
EULA is an agreement between you as an owner and a user of your product. In brief, it contains:
- What the users can do with the app, and what they aren't allowed to do
- Licensing fees
- Intellectual property information, etc.
Terms of Use or Terms and Conditions explain what services you offer the users and how you expect them to behave in return. Though Google doesn’t demand Terms of Use, it’s better to publish them. You can create one document, adding there Privacy Policy and Terms of Use chapters.
Pay special attention to include in the Privacy Policy the following information:
- A complete list of personal data that is collected, processed and used through the app
- Technical information that is collected about the device and the installed OS
- Functional features of the app, its paid and free functionality
- Place of registration of the company and/or location of the copyright holder of the application
- The chosen legal system and legislation that will be applied in resolving disputes and regulating legal relations
- The terms of subscription
- Citizenship (residence) of the overwhelming majority of application users
- Age criteria, the presence of specific content
Step 4: Study Google Developer Policies
We guess you already made up your product concept. Now it’s time to make sure that every feature you will implement in the app is aligned with the Google Developer Policies. These documents explain how mobile apps need to be developed, updated, and promoted to support the store's high-quality standards.
If Google decides that your product violates some policy chapters, it may be rejected, blocked, or even deleted from Google Play. Besides, numerous and repetitive violations may lead to the developer account termination.
So study all the available information carefully about:
- Restricted content definition
- App store listing and promotion
- Impersonation and intellectual property
- Rules for monetization and ads
- Privacy, security and deception regulation
- Spam and minimum functionality
Google is constantly working on its policies, and it’s important to monitor the changes and stay up to date even after your Android app is released.
Step 5: Technical Requirements
You went through the development process, endless testing, and bug fixing, and finally, the “X-day” comes. Before moving on to the upload process, you need to check the following things:
The package name should be suitable over the life of your application. You cannot change it after the distribution. You can set the package name in the application's manifest file.
- Signed App Release With a Signing Certificate
Every application should be digitally signed with a developer's certificate. The certificate is used to identify the author of an app and can’t be generated again.
Google set the limit size of the uploaded file: 100MB for Android 2.3 and higher (API level 9-10, 14 and higher) and 50MB for lower Android versions.
If your app exceeds this limit, you can always switch to APK Expansion Files.
Two possible release formats are accepted by Google: app bundle and .apk. However, .aab is the preferred one. To use this format, you need to enroll in app signing by Google Play.
You may learn more about app file technical requirements in the Developer Documents, Prepare for the release guide.
Step 6: Creating the App on the Google Console
Now you have the file that is ready for uploading. It’s time to get to the fun part. Let’s create a new app in your Developer Account:
- Reach to All applications tab in the menu
- Now select Create Application
- Choose the app’s default language from the drop-down menu
- Add a brief app description (you can change it later)
- Tap on Create
After this, you will be taken to the store entry page, where we will add the complete data about the app.
Step 7: Store Listing
First, let’s prepare the Store listing. It contains the most important information useful for app store optimization (ASO) and gives the users more details about your app before downloading. The mandatory sections are marked with *.
You may need some designer and copywriter efforts, so it’s better to start preparing the following materials in advance.
It contains a title of your app (up to 50 symbols), a brief description (up to 80 symbols), and a full description (up to 4000 symbols). Control yourself and do not overdo the keywords.
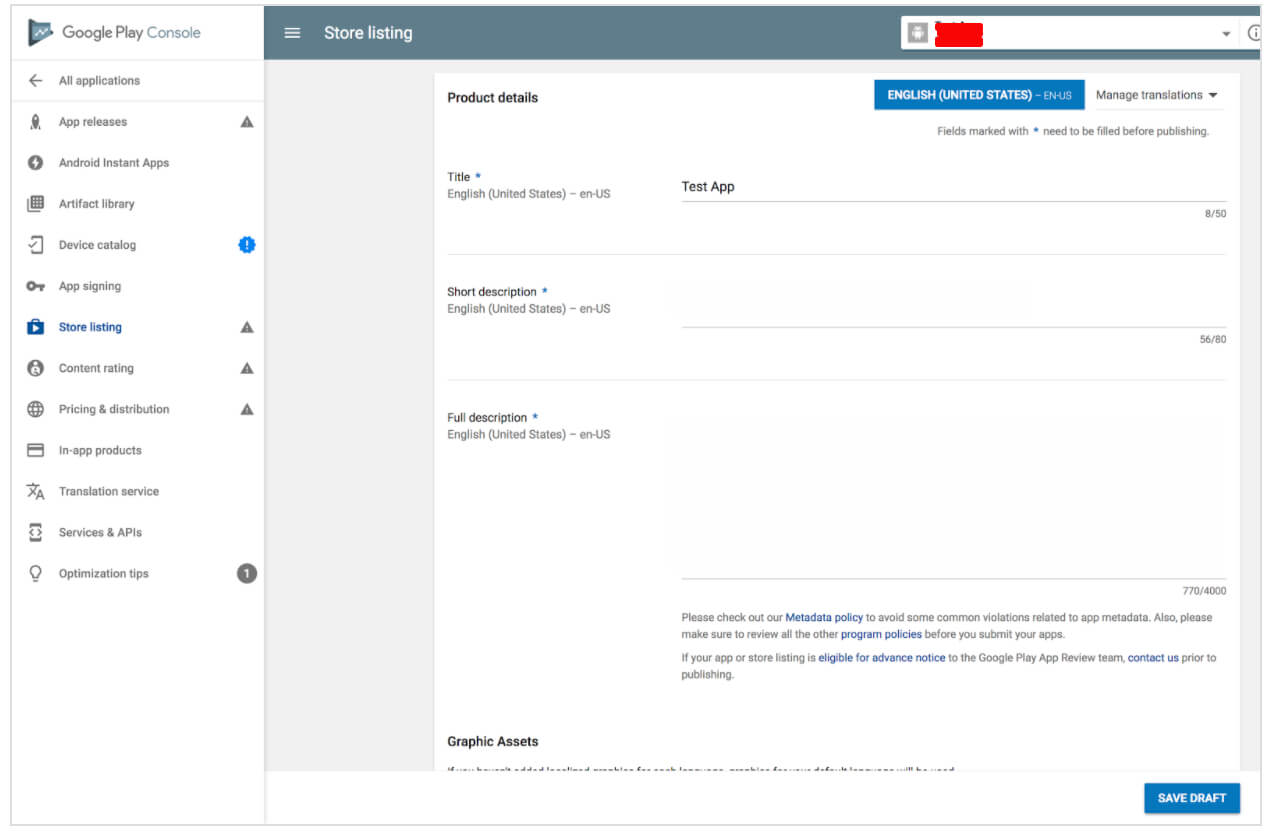
Store listing
You may add from 2 to 8 screenshots. Choose the ones that show the app functionality and value the most.
The requirements are the following:
- JPEG or 24-bit PNG (no alpha)
- from 320px to 3840 px
- the ratio of the long side to the short side should not be more than 2:1
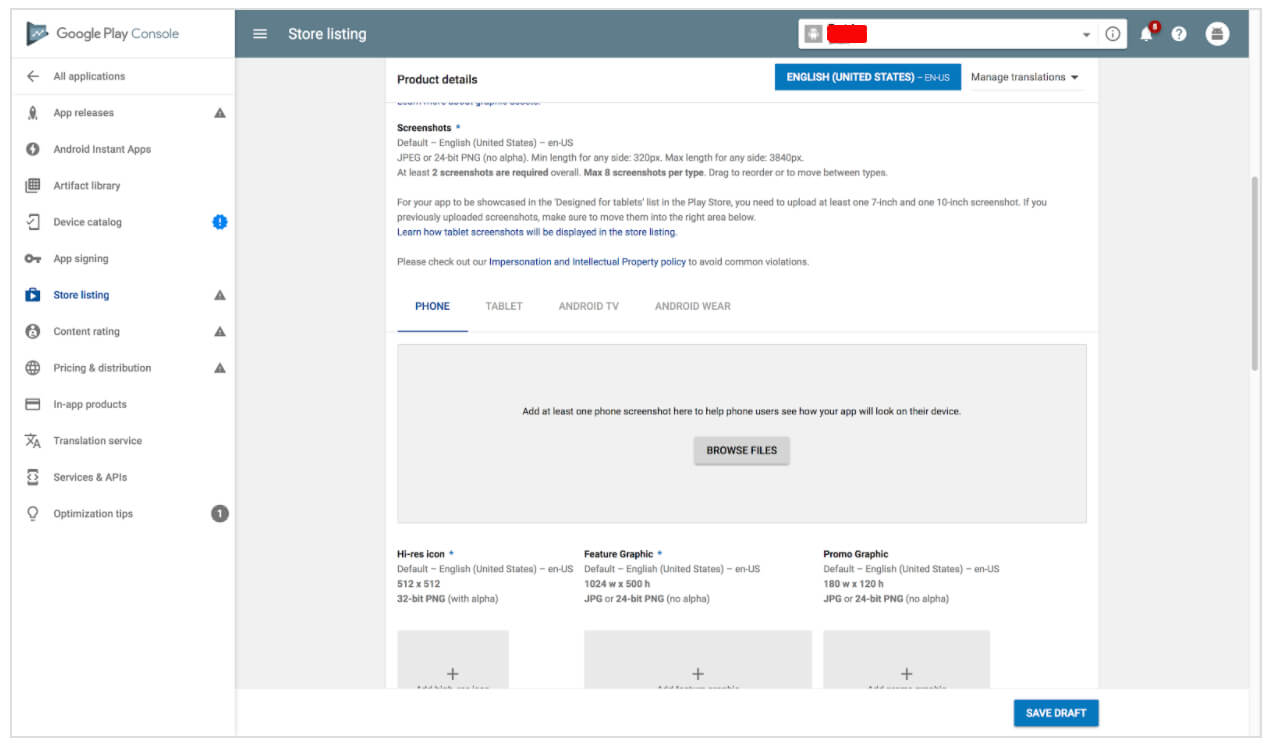
Store listing - Product details
The requirements are the following:
- 512px by 512px
- 32-bit PNG (with alpha)
- Maximum file size: 1024KB
It is an optional marketing tool displayed in various places on Google Play, for example, on the homepage.
The requirements are the following:
- JPEG or 24-bit PNG (no alpha)
- 1024px x 500px
If you have any promo video, you may add a link to your YouTube channel. This video will be shown before the screenshots on the app’s page.
You may choose from the list the most relevant to your app keywords for better ASO. There is no possibility to add any custom tags.
If your app supports several languages, mention all of them and add translations of your app’s information. It’s highly recommended to include localized screenshots and images.
- Application type and categorization
First, through the drop-down menu, select the application type: game or app. Then pick the category that your app fits into. You can also add a section to rate your content after uploading APK to Google Play store.
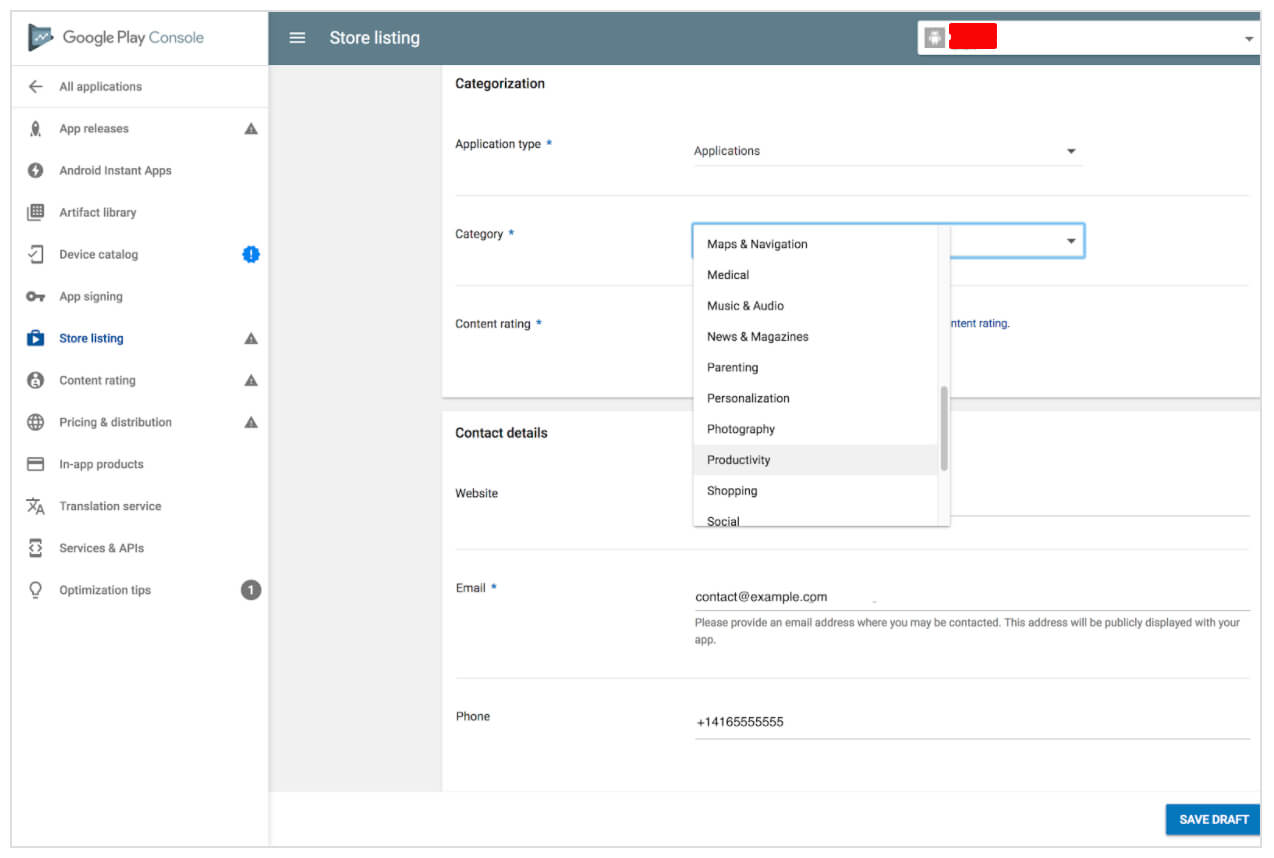
App categories on Google Play
Here you should provide the support service contacts. By filling the website URL, email, and phone, you make it easier for the users to contact you if necessary.
Google requires you to add a link to the Privacy Policy that we discussed above.
While editing the Store Listing, you can take a break at any moment, click Save Draft, and complete this stage later.
Step 8: Content Rating
In order not to be marked as an Unrated App (that may lead to app removal), pass a rating questionnaire. You can easily find this section on the left-side menu.
The information provided in the questionnaire must be accurate. Any misrepresentation of your app’s content might lead to suspension or removal of the Google Play account.
- Click on Save Questionnaire once you complete the survey
- Click on Calculate Rating
- In the end, click on Apply Rating to confirm the rating and move forward with the pricing & distribution plan
Step 9: Pricing the Application
In the Pricing and distribution section, you need to fill the following information:
- Whether your app is free or paid
- Where the app will be available (just choose the countries from the list)
- Whether your app will be available only on the specific devices
- Whether the app has sensitive content and is not suitable for children under the age of 13
- Whether your app contains ads
Remember that you can change your paid app to a free one later, but you cannot do the vice versa. If you decide later that you want to distribute the app for money, you’ll have to create another app.
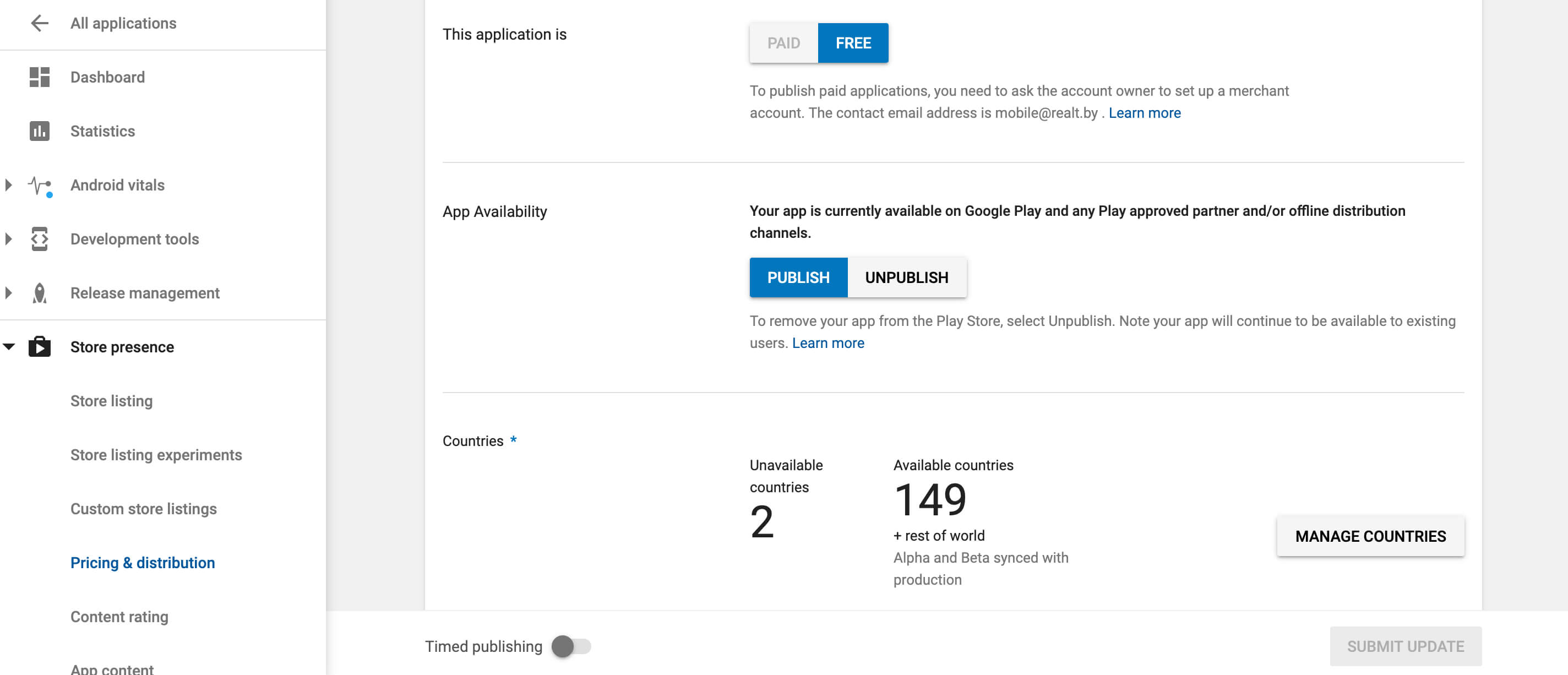
Store presence
Step 10: Upload APK and Send for Review
Finally, you are ready to upload your Android app file. That’s the most exciting moment ever.
Let’s go to the App Releases section on the left panel. Here you will find three options for publishing the app: Production, Beta and Alpha tracks.
We highly recommend starting with Alpha or Beta versions. In this case, after passing the review process, your app will not be available to everyone on the Google Play store.
The Alpha version assumes closed testing and is available only to those who you invite as testers. The Beta version means that anyone can join your testing program and send feedback to you.
Pre-release testing allows you to gather people’s opinions, test your app in a broader audience, and fix issues before making the app public.
Note that if you decide later to change the Alpha or Beta version to Production type, it will take time to go through another review round.
Once you choose the type of release, follow the steps:
- Choose Manage (Production/Beta/Alpha)
- Click on Edit Release
- Upload an APK or app bundle
The release name will be added automatically. For the first time, you may delete the text from the What’s new in this release field.
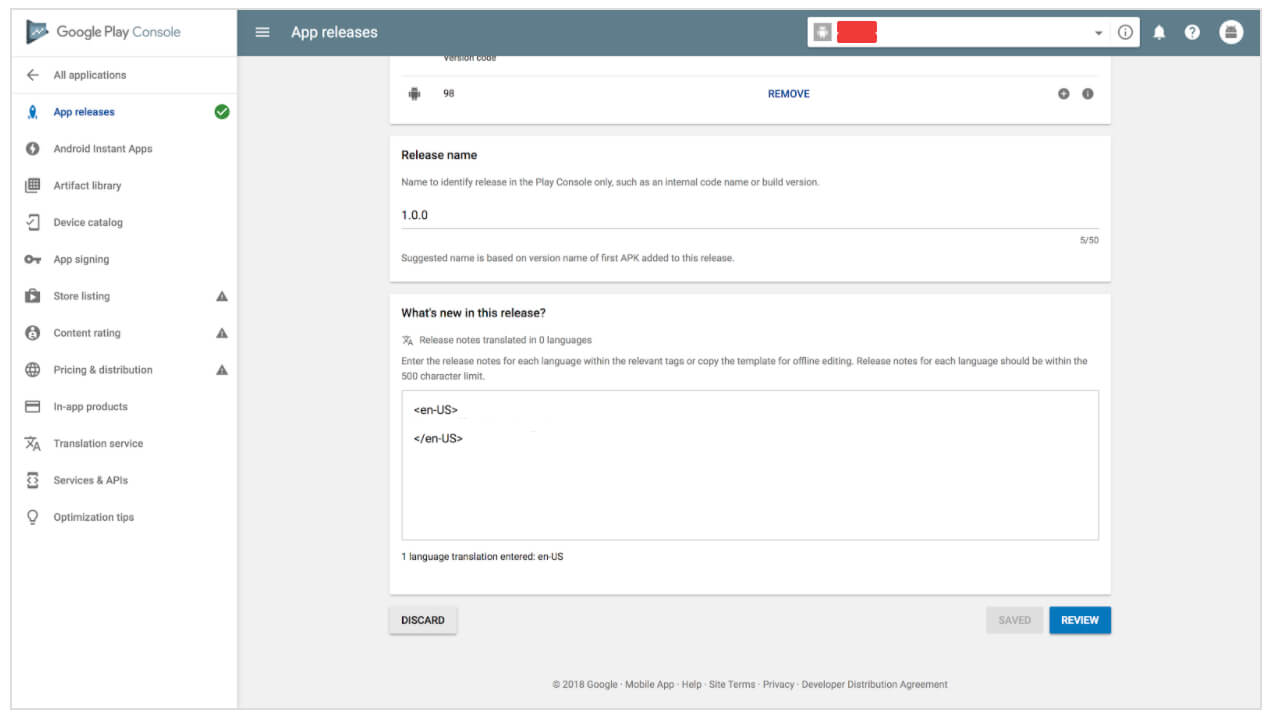
App releases
- Click on Review to confirm the changes and send your app to the review by pressing Start rollout to production.
Don’t worry that you may forget to add some information. All the way, Google will show you the instructions and tips. Actually, you won’t manage to send the app to the review if something important is missed.
Remember that with the very first version, there is no opportunity to set manual publishing. The app will be released right after it passes the review. Usually, it takes up to 2 days. Google says the review process could take up to 7 days or even longer.
Once the app is reviewed, you’ll receive a notification on Google Console Dashboard.
Wrapping Up
We hope these instructions will help you to get through the publishing process easily, and soon the Google Play Store users can download your very special Android app.
But remember that the journey does not stop at publishing. Running a mobile application requires continuous efforts to get it trending, otherwise competition will overshadow the app.
Let’s discuss your mobile app strategy. Our experts will help you in making it a success!
Thanks for reading!
SYED CS HUB ❤️







Comments
Post a Comment